Vuex 개요
2018-04-18
Veux 개요
- Vuex 라이브러리 등장 배경
- Vuex 라이브러리의 주요 속성인 state(data), getters(computed), mutations(methods), actions(async methods)
- Vuex를 더 쉽게 사용할 수 있는 Helper
- Vuex로 프로젝트를 구조화 하는 방법 및 모듈 구조화 방법
목차
- Vuex 소개
- Flux 패턴 소개
- Vuex 컨셉과 구조
- Vuex 기술 요소 (state, getters, mutations, actions)
- Vuex Helpers
- Vuex 구조화
Vuex가 왜 필요할까?
- 복잡한 애플리케이션에서 컴포넌트의 개수가 많아지면 컴포넌트 간에 데이터 전달이 어려워 진다.
-
Ex. 하위 컴포넌트에서 다른 컴포넌트로 데이터를 전달하려 할때
- 이벤트 버스로 해결?
- 어디서 이벤트를 보냈는지 혹은 어디서 이벤트를 받았는지 알기 어려움
// Login.Vue eventBus.$emit('fetch', loginInfo); // List.vue eventBus.$on('display', data => this.displayOnScreen(data)); // Chart.vue eventBus.$emit('refreshData', ChartData);- 컴포넌트 간 데이터 전달이 명시적이지 않음
Vuex로 해결할 수 있는 문제
- MVC 패턴에서 발생하는 구조적 오류
- 컴포넌트 간 데이터 전달 명시
- 여러 개의 컴포넌트에서 같은 데이터를 업데이트 할 때 동기화 문제
Vuex 컨셉
- State: 컴포넌트 간에 공유하는 데이
data()- State는 앱을 작동하는 원본 소스
- View: 데이터를 표시하는 화면
template- View는 State의 선언적 매핑
- Action: 사용자의 입력에 따라 데이터를 변경하는
methods- Action은 View 에서 사용자 입력에 대해 반응적으로 상태를 바꾸는 방법
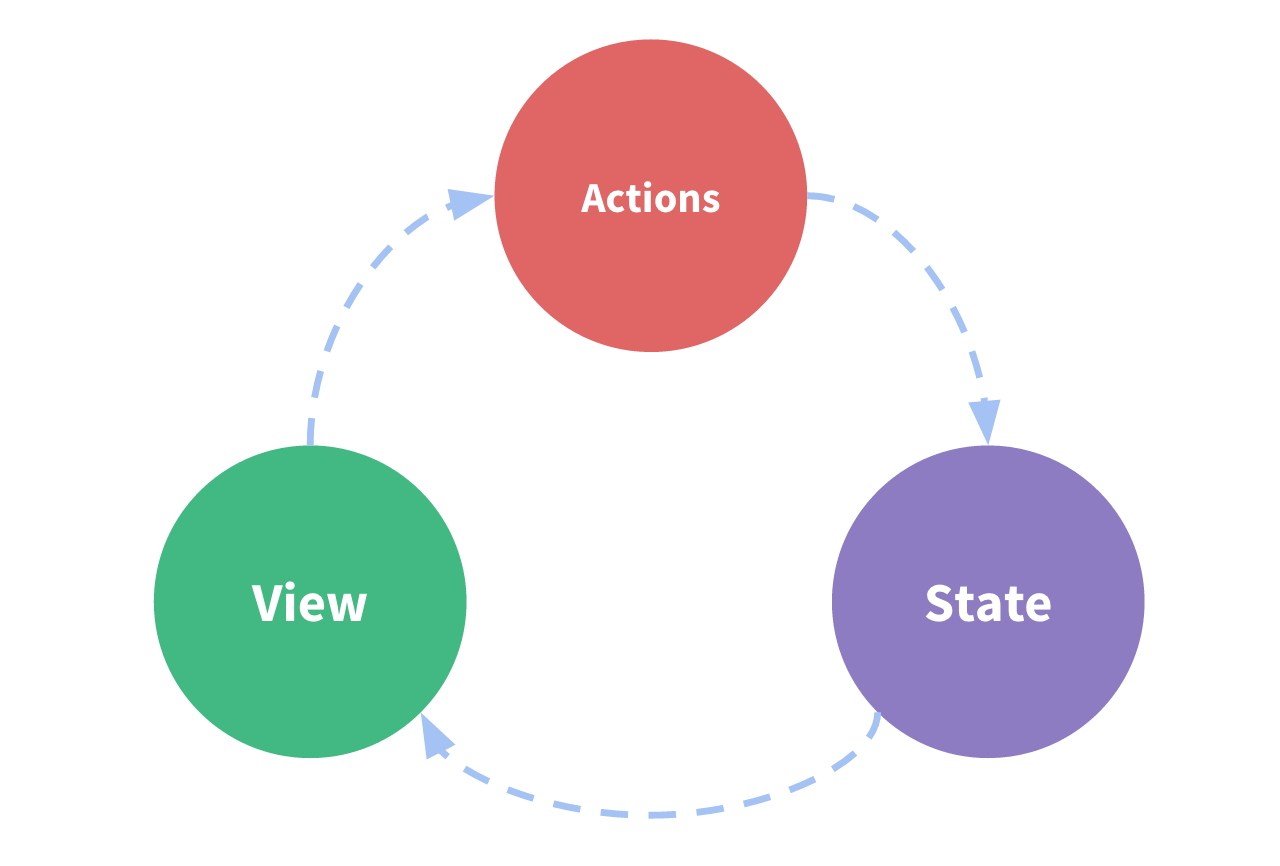 Action -> State -> View -> Action
Action -> State -> View -> Action
Vuex 구조
- 컴포넌트 -> 비동기 로직 -> 동기 로직 -> 상태
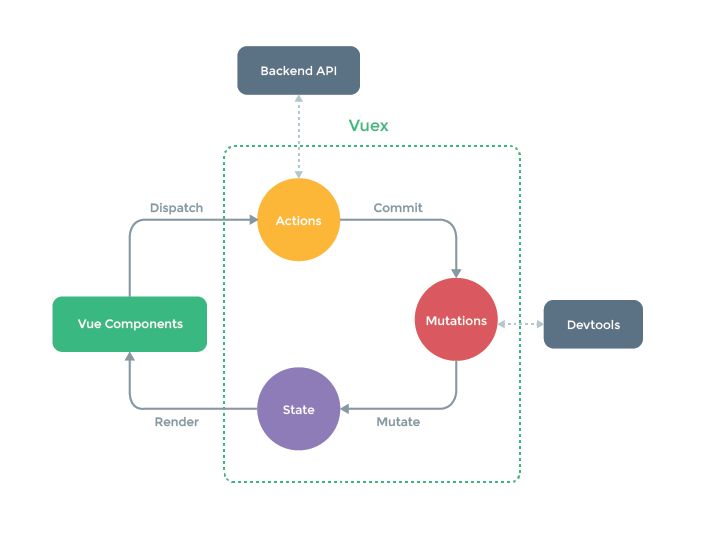
Vuex 기술 요소
- state: 여러 컴포넌트에 공유되는 데이
data - getters: 연산된 state 값을 접근하는 속성
computed - mutations: state 값을 변경하는 이벤트 로직, 메서드
methods - actions: 비동기 처리 로직을 선언하는 메서드
async methods
State 란?
- 여러 컴포넌트 간에 공유할 데이터 - 상태
// Vue
data: {
message: 'hi'
}
// Vuex
state: {
message: 'hi'
}
<!-- Vue -->
<p>{{ message }}</p>
<!-- Vuex -->
<p>{{ this.$store.state.message }}</p>
Getters 란?
- state 값을 접근하는 속성이자
computed()처럼 미리 연산된 값을 접근하는 속성
// store.js
state: {
num: 10
},
getters: {
getNumber(state) {
return state.num;
},
doubleNumber(state) {
return state.num * 2;
}
}
<p>{{ this.$store.getters.getNumber }}</p>
<p>{{ this.$store.getters.doubleNumber }}</p>
mutations 란?
- state의 값을 변경할 수 있는 유일한 방법 이자 메서드
- mutations
commit()으로 동작시킨다.
// store.js
state: {num:10},
mutations: {
printNumbers(state) { // 첫번째 인자 state는 고정
return state.num
},
sumNumbers(state, anotherNum) {
return state.num + anotherNum;
}
}
// App.vue
this.$store.commit('printNumbers');
this.$store.commit('sumNumbers', 20); // 20은 anotherNum에 해당
mutations의 commit() 형식
- state를 변경하기 위해 mutations를 동작시킬 때 인자(payload)를 전달할 수 있음.
// store.js
state: { storeNum: 10 },
mutations: {
modifyState(state, payload) {
console.log(payload.str);
return state.storeNum += payload.num;
})
}
// App.vue
this.$store.commit('modifyState', {
// 여러인자를 보낼때는 object 이용
str: 'passed from payload',
num: 20
});
state는 왜 직접 변경하지 않고 mutations로 변경할까??
- 여러 개의 컴포넌트에서 아래와 같이 state 값을 변경하는 경우 어느 컴포넌트에서 해당 state를 변경하기 추적하기가 어렵다.
methods: {
increaseCounter() {
this.$store.state.counter++;
}
}
- 특정 시점에 어떤 컴포넌트가 state를 접근하여 변경한 건지 확인하기 어렵기 때문
- 따라서, 뷰의 반응성을 거스르지 않게 명시적으로 상태 변화를 수행. 반응성, 디버깅, 테스팅 혜택
actions 란?
- 비동기 처리 로직을 선언하는 메서드. 비동기 로직을 담당하는 mutations의 스핀오프 버전
- 데이터 요청, Promise, ES6 async 같은 비동기 처리는 모두 actions에 선언
- actions에서 mutations 접근 가능
// store.js
state: { num: 10 },
mutations: {
doubleNumber(state) {
return state.num * 2;
}
},
actions: {
delayDoubleNumber(context) { // context로 store의 메서드와 속성 접근 가능
context.commit('doubleNumber');
}
}
// App.vue
this.$store.dispatch('delayDoubleNumber');
actions 비동기 코드 예제 1
// store.js
mutations: {
addCounter(state) {
state.counter++;
},
},
actions: {
delayAddCounter(context) { // context로 store의 메서드와 속성 접근 가능
setTimeout(() => context.commit('addCounter'), 2000);
}
}
// App.vue
methods: {
incrementCounter() {
this.$store.dispatch('delayAddCounter');
}
}
actions 비동기 코드 예제 2
- 실제 서버에서 데이터를 불러와 연동하는 경우
// store.js
mutations: {
setData(state, fetchedData) {
state.product = fetchedData;
}
},
actions: {
fetchProductData(context) {
return axios.get('https://google.com').then(res => context.commit('setData'), res);
}
}
// App.vue
methods: {
getProduct() {
this.$store.dispatch('fetchProductData')
}
}
왜 비동기 처리 로직은 actions에 선언해야 할까?
- 언제 어느 컴포넌트에서 해당 state를 호출하고, 변경했는지 확인하기가 어려움
- 어느 컴포넌트에서 무엇을 호출했는지 컴포넌트의 수가 많아질 수록 어려워 진다.
결론: state 값의 변화를 추적하기 어렵기 때문에 mutations 속성에는 동기 처리 로직만 넣는다.
각 속성들을 더 쉽게 사용하는 방법 - Helper
- store에 있는 4가지 속성들을 간편하게 사용하는 방법
- state -> mapState
- getters -> mapGetters
- mutations -> mapMutations
- actions -> mapActions
헬퍼의 사용법
- 헬퍼를 사용하고자 vue 파일에서 아래와 같이 해당 헬퍼를 로딩
// App.vue
import { mapState, mapGetters, mapMutations, mapActions } from 'vuex';
export default {
computed() { ...mapState(['num']), ...mapGetters(['countedNum']) },
methods: { ...mapMutations(['clickBtn']), ...mapAtcions(['asyncClickBtn']) }
}
펼침연산자 사용 이유
- 기존의 속성과 함께 사용하기 위해
mapState 사용 예
- Vuex에 선언한 state 속성을 뷰 컴포넌트에 쉽게 연결해주는 헬퍼
// App.vue
import { mapState } from 'vuex';
computed() {
...mapState(['num'])
// num() { return this.$store.state.num }
}
// store.js
state: { num: 10 }
<!-- <p>{{ this.$store.state.num }}</p> -->
<p>{{this.num}}</p>
mapGetters 사용 예
- Vuex에 선언한 getters 속성을 뷰 컴포넌트에 쉽게 연결해주는 헬퍼
// App.vue
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex';
computed() {
...mapGetters(['reverseMessage'])
// getters의 함수명과 템플릿에서 사용할 이름을 다르게 하고싶다면 객체로
// ...mapGetters({
// revMsg: 'reverseMessage'
//})
}
// store.js
getters: {
reverseMessage(state) {
return state.msg.split('').revsere().join('');
}
}
<!-- <p>{{ this.$store.getters.reverseMessage }}</p> -->
<p>{{ this.reverseMessage }}</p>
mapMutations
- Vuex에 선언한 mutations 속성을 뷰 컴포넌트에 쉽게 연결해주는 헬퍼
// App.vue
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex';
methods: {
...mapMutations(['clickBtn']),
authLogin() {},
displayTable() {}
}
// store.js
mutations: {
clickBtn(state) {
alert(state.msg);
}
}
<button @click="clickBtn">popup msg</button>
mapActions
- Vuex에 선언한 actions 속성을 뷰 컴포넌트에 쉽게 연결해주는 헬퍼
// App.vue
import { mapActions } from 'vuex';
methods: {
...mapActions(['delayClickBtn']),
}
// store.js
actions: {
delayClickBtn(context) {
setTimeout(() => context.commit('clickBtn'), 2000);
}
}
<button @click="delayClickBtn">delay popup msg</button>
헬퍼의 유연한 문법
- Vuex에 선언한 속성을 그대로 컴포넌트에 연결하는 문법
// 배열 리터럴
...mapMutations([
'clickBtn', // 'clickBtn': clickBtn
'addNumber' // addNumber(인자) 인자는 자동으로 넘어감
])
- Vuex에 선언한 속성을 컴포넌트의 특정 메서드에 연결하는 문법
// 객체 리터럴
...mapMutations({
popupMsg: 'clickBtn' // 컴포넌트 메서드 명 : Store의 mutations 명
})
프로젝트 구조화와 모듈화 방법 1
- before
// store.js
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
export const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {},
getters: {},
mutations: {},
actions: {}
})
- after ES6 import & export 사용
// store.js
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
import * as getters from 'store/getters.js';
import * as mutations from 'store/mutations.js';
import * as actions from 'store/actions.js';
export const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {},
getters: getters,
mutations: mutations,
actions: actions
})
프로젝트 구조화와 모듈화 방법 2
- 앱이 비대해져서 1개의 store로 관리하기 힘들때 modules속성 사용
// store.js
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
import todo from 'modules/todo.js';
export const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
moduleA: todo, // 모듈 명칭: 모듈 파일명
todo // todo: todo
}
})
// todo.js
const state = {}
const getters = {}
const mutations = {}
const actions = {}
export default {
state,
getters,
mutations,
actions
}